The aim of this Masterclass is to train users to perform and analyze a metadynamics simulation with PLUMED.
Once this Masterclass is completed, users will be able to:
PLUMED can be used not only to analyze a pre-existing MD trajectory, but also to add forces on the CVs during a MD simulation, for example, in order to accelerate sampling. To this aim, we have implemented a variety of possible biases acting on CVs. The complete documentation for all the biasing methods available in PLUMED can be found at the Bias page. In the following we will learn how to use PLUMED to perform and analyze a metadynamics simulation. The users are invited to familiarize with the theory behind this method by looking at one of the many reviews available, such as [74] [12] [120] [29]. Below you can find a brief recap of the basic metadynamics theory.
In metadynamics, an external history-dependent bias potential is constructed in the space of a few selected degrees of freedom \( \vec{s}({q})\), generally called collective variables (CVs) [75]. This potential is built as a sum of Gaussian kernels deposited along the trajectory in the CVs space:
\[ V(\vec{s},t) = \sum_{ k \tau < t} W(k \tau) \exp\left( -\sum_{i=1}^{d} \frac{(s_i-s_i({q}(k \tau)))^2}{2\sigma_i^2} \right). \]
where \( \tau \) is the Gaussian deposition stride, \( \sigma_i \) the width of the Gaussian for the \(i\)th CV, and \( W(k \tau) \) the height of the Gaussian. The effect of the metadynamics bias potential is to push the system away from local minima into visiting new regions of the phase space. Furthermore, in the long time limit, the bias potential converges to minus the free energy as a function of the CVs:
\[ V(\vec{s},t\rightarrow \infty) = -F(\vec{s}) + C. \]
In standard metadynamics, Gaussian kernels of constant height are added for the entire course of a simulation. As a result, the system is eventually pushed to explore high free-energy regions and the estimate of the free energy calculated from the bias potential oscillates around the real value. In well-tempered metadynamics [11], the height of the Gaussian is decreased with simulation time according to:
\[ W (k \tau ) = W_0 \exp \left( -\frac{V(\vec{s}({q}(k \tau)),k \tau)}{k_B\Delta T} \right ), \]
where \( W_0 \) is an initial Gaussian height, \( \Delta T \) an input parameter with the dimension of a temperature, and \( k_B \) the Boltzmann constant. With this rescaling of the Gaussian height, the bias potential smoothly converges in the long time limit, but it does not fully compensate the underlying free energy:
\[ V(\vec{s},t\rightarrow \infty) = -\frac{\Delta T}{T+\Delta T}F(\vec{s}) + C. \]
where \( T \) is the temperature of the system. In the long time limit, the CVs thus sample an ensemble at a temperature \( T+\Delta T \) which is higher than the system temperature \( T \). The parameter \( \Delta T \) can be chosen to regulate the extent of free-energy exploration: \( \Delta T = 0\) corresponds to standard MD, \( \Delta T \rightarrow\infty\) to standard metadynamics. In well-tempered metadynamics literature and in PLUMED, you will often encounter the term "bias factor" which is the ratio between the temperature of the CVs ( \( T+\Delta T \)) and the system temperature ( \( T \)):
\[ \gamma = \frac{T+\Delta T}{T}. \]
The bias factor should thus be carefully chosen in order for the relevant free-energy barriers to be crossed efficiently in the time scale of the simulation.
Additional information can be found in the several review papers on metadynamics [74] [12] [120] [29].
The users can refer to the procedure introduce in PLUMED Masterclass 21.1: PLUMED syntax and analysis and PLUMED Masterclass 21.3: Umbrella sampling to install the required software. In this class, we will perform the simulations ourselves, so make sure that the GROMACS code is properly installed.
The data needed to complete the exercises of this Masterclass can be found on GitHub. You can clone this repository locally on your machine using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/plumed/masterclass-21-4.git
This repositoy contains 3 folders:
data: GROMACS topology/PDB files for the two systems that we are going to simulate and python script for error analysis;notebooks: Jupyter notebook to be used as template for the analysis of the PLUMED output;slides: a brief presentation of the metadynamics theory. To keep things clean, it is recommended to run each exercise in a separate sub-directory (i.e. Exercise-1, Exercise-2, ...), which you can create inside the root directory masterclass-21-4. The students are invited to solve the exercises by themselves after completing the PLUMED input file templates provided below. In case of problems, students can rely on the solution notebook solution.ipynb provided in the GitHub repository.
In many exercises, we will play with a toy system, alanine dipeptide simulated in vacuo (see Fig. master-ISDD-2-ala-fig). This rather simple molecule is useful to understand data analysis and free-energy methods. This system is a nice example because it presents two metastable states separated by a high free-energy barrier. It is conventional use to characterize the two states in terms of Ramachandran dihedral angles, which are denoted with \( \phi \) (phi) and \( \psi \) (psi) in Fig. master-ISDD-2-transition-fig. In the data/diala directory of the GitHub repository for this Masterclass, you will find two GROMACS .tpr files (topolA.tpr and topolB.tpr), which contain all the necessary information to perform a simulation starting from either one of the two metastable states of alanine dipeptide.


In this brief exercise, we will perform two 20 ns long standard MD simulations of alanine dipeptide starting from the two main metastable states of this system. To keep things clean, the users are invited to run these two simulations in two separate sub-folders. To run these simulations with GROMACS, please use the following commands:
# run this command in one directory gmx mdrun -s topolA.tpr -nsteps 10000000 # and this in another one gmx mdrun -s topolB.tpr -nsteps 10000000
After the simulations are completed, we can use PLUMED to monitor the behavior of the system. As learnt in PLUMED Masterclass 21.1: PLUMED syntax and analysis, PLUMED can compute and print collective variables (CVs) on a pre-calculated MD trajectory. Here, we will:
Let's now prepare a PLUMED input file to calculate:
by completing the template below (whenever you see an highlighted FILL string, this is a string that you must replace!):

# Activate MOLINFO functionalities MOLINFOSTRUCTURE=__FILL__ # Compute the backbone dihedral angle phi, defined by atoms C-N-CA-C # you should use MOLINFO shortcuts phi: TORSIONcompulsory keyword a file in pdb format containing a reference structure.ATOMS=__FILL__ # Compute the backbone dihedral angle psi, defined by atoms N-CA-C-N # here also you should to use MOLINFO shortcuts psi: TORSIONthe four atoms involved in the torsional angleATOMS=__FILL__ # Print the two collective variables on COLVAR file every step PRINTthe four atoms involved in the torsional angleARG=__FILL__the input for this action is the scalar output from one or more other actions.FILE=COLVARthe name of the file on which to output these quantitiesSTRIDE=__FILL__compulsory keyword ( default=1 ) the frequency with which the quantities of interest should be output
Once your plumed.dat file is complete, you can run the PLUMED driver on the two MD trajectories as follows:
plumed driver --plumed plumed.dat --mf_xtc traj_comp.xtc
The two COLVAR files can be analyzed using the Jupyter notebook plumed-pandas.ipynb provided in the folder notebooks. This notebook allows you to import a COLVAR file produced by PLUMED and to generate the desired figures using the matplotlib library. The users are invited to:
Are both simulations long enough to visit all the relevant conformations or instead they remain trapped in different regions of the \( \phi \) / \( \psi \) space?
In this exercise we will setup and perform a well-tempered metadynamics run using the backbone dihedral \( \phi \) as collective variable. During the calculation, we will also monitor the behavior of the other backbone dihedral \( \psi \). Here you can find a sample plumed.dat file that you can use as a template.

# Activate MOLINFO functionalities MOLINFOSTRUCTURE=__FILL__ # Compute the backbone dihedral angle phi, defined by atoms C-N-CA-C # you should use MOLINFO shortcuts phi: TORSIONcompulsory keyword a file in pdb format containing a reference structure.ATOMS=__FILL__ # Compute the backbone dihedral angle psi, defined by atoms N-CA-C-N # here also you should to use MOLINFO shortcuts psi: TORSIONthe four atoms involved in the torsional angleATOMS=__FILL__ # Activate well-tempered metadynamics in phi metad: __FILL__the four atoms involved in the torsional angleARG=__FILL__ # Deposit a Gaussian every 500 time steps, with initial height # equal to 1.2 kJ/mol and bias factor equal to 8could not find this keywordPACE=500could not find this keywordHEIGHT=1.2could not find this keywordBIASFACTOR=8 # Gaussian width (sigma) should be chosen based on the CV fluctuations in unbiased run # try 1/2 or 1/3 of the estimated fluctuationscould not find this keywordSIGMA=__FILL__ # Gaussians will be written to file and also stored on gridcould not find this keywordFILE=HILLScould not find this keywordGRID_MIN=-picould not find this keywordGRID_MAX=pi ... # Print both collective variables on COLVAR file every 10 steps PRINTcould not find this keywordARG=__FILL__the input for this action is the scalar output from one or more other actions.FILE=COLVARthe name of the file on which to output these quantitiesSTRIDE=__FILL__compulsory keyword ( default=1 ) the frequency with which the quantities of interest should be output
Once your plumed.dat file is complete, you can run a 20 ns long metadynamics simulations starting from either of the two provided conformations, for example topolA.tpr. All you need to do is execute the following command:
gmx mdrun -s topolA.tpr -nsteps 10000000 -plumed plumed.dat
During the metadynamics simulation, PLUMED will create two files, named COLVAR and HILLS. The COLVAR file contains all the information specified by the PRINT command, in this case the value of the backbone dihedrals \( \phi \) and \( \psi \) every 10 steps of simulation. The HILLS file contains a list of the Gaussian kernels deposited along the simulation.
Let's visualize the time series of the two collective variables. Take your time to inspect the behavior of the two CVs. What are the main differences with respect to the trajectory produced in Exercise 1: Familiarizing with alanine dipeptide ?
At this point, we can estimate the free energy as a function of the metadynamics CV directly from the metadynamics bias potential. In order to do so, the utility sum_hills can be used to sum the Gaussian kernels deposited during the simulation and stored in the HILLS file.
To calculate the free energy as a function of \( \phi \), it is sufficient to use the following command line:
plumed sum_hills --hills HILLS
The command above generates a file called fes.dat in which the free-energy surface as function of \( \phi \) is calculated on a regular grid. One can modify the default name for the free-energy file, as well as the boundaries and bin size of the grid, by using the following sum_hills options:
--outfile - specify the outputfile for sumhills --min - the lower bounds for the grid --max - the upper bounds for the grid --bin - the number of bins for the grid --spacing - grid spacing, alternative to the number of bins
To give a preliminary assessment of the convergence of a metadynamics simulation, one can calculate the estimate of the free energy as a function of simulation time. At convergence, the reconstructed profiles should be similar. The sum_hills option --stride should be used to give an estimate of the free energy every N Gaussian kernels deposited, and the option --mintozero can be used to align the profiles by setting the global minimum to zero. If we use the following command line:
plumed sum_hills --hills HILLS --stride 200 --mintozero
one free energy is calculated every 200 Gaussian kernels deposited, and the global minimum is set to zero in all profiles. Now, you can visualize the free-energy estimate as a function of simulation time and assess how it changed during the course of the simulation. In the last part of this 20 ns long metadynamics simulation, the free-energy estimate should not change significantly.
Looking at the time-evolution of the entire free-energy profile might not be straightforward. Therefore, what we usually do is focusing on a few metastable states, or local free-energy minima, and calculating their estimated free-energy difference as a function of time. In case of alanine dipeptide, this is rather easy since there are only two major states in the free-energy profile as a function of the CV \(\phi\).
The users should now:
These two observations:
are two indications that the simulation might have converged.
In the previous exercise we biased \(\phi\) and computed the free energy as a function of the same variable directly from the metadynamics bias potential using the sum_hills utility. However, in many cases you might decide which variable should be analyzed after having performed a metadynamics simulation. For example, you might want to calculate the free energy as a function of CVs other than those biased during the metadynamics simulation, such as the dihedral \( \psi \). At variance with standard MD simulations, you cannot simply calculate histograms of other variables directly from your metadynamics trajectory, because the presence of the metadynamics bias potential has altered the statistical weight of each frame. To remove the effect of this bias and thus be able to calculate properties of the system in the unbiased ensemble, you must reweight (unbias) your simulation.
There are multiple ways to calculate the correct statistical weight of each frame in your metadynamics trajectory and thus to reweight your simulation. For example:
In this exercise we will use the second method, which is identical to the umbrella-sampling reweighting approach that you have already used in PLUMED Masterclass 21.2: Statistical errors in MD and PLUMED Masterclass 21.3: Umbrella sampling. In order to compute the weights we will use the driver tool.
First of all, you need to prepare a plumed_reweight.dat file that is identical to the one you used for running your metadynamics simulation except for a few modifications:
RESTART=YES to the METAD command. This will make this action behave as if PLUMED was restarting, i.e. PLUMED will read from the HILLS file the Gaussians that have previously been accumulated;HEIGHT to zero and the PACE to a large number. This will actually avoid adding new Gaussians (and even if they are added they will have zero height);phi and psi, you also write metad.bias;COLVAR_REWEIGHT.Here how the plumed_reweight.dat should look like:

# Activate MOLINFO functionalities MOLINFOSTRUCTURE=__FILL__ __FILL__ # here goes the definitions of the phi and psi CVs # Activate well-tempered metadynamics in phi metad: __FILL__compulsory keyword a file in pdb format containing a reference structure.ARG=__FILL__ # Deposit a Gaussian every 10000000 time steps (never!), with initial height equal to 0.0 kJ/molcould not find this keywordPACE=10000000could not find this keywordHEIGHT=0.0 # <- this is the new stuff! # The bias factor and Gaussian width are the same as beforecould not find this keywordBIASFACTOR=__FILL__could not find this keywordSIGMA=__FILL__ # Gaussians will be read from file and stored on grid # Make sure you specify the path the HILLS file produced in Exercise 2!could not find this keywordFILE=HILLScould not find this keywordGRID_MIN=-picould not find this keywordGRID_MAX=pi # Say that METAD should be restarting (= reading an existing HILLS file)could not find this keywordRESTART=YES # <- this is the new stuff! ... # Print out the values of phi, psi and the metadynamics bias potential # Make sure you print out the 3 variables in the specified order at every step PRINTcould not find this keywordARG=__FILL__the input for this action is the scalar output from one or more other actions.FILE=COLVAR_REWEIGHTthe name of the file on which to output these quantitiesSTRIDE=__FILL__ # <- also change this one!compulsory keyword ( default=1 ) the frequency with which the quantities of interest should be output
Now you can run the driver tool using this command:
plumed driver --mf_xtc traj_comp.xtc --plumed plumed_reweight.dat --kt 2.494339
where traj_comp.xtc is the metadynamics trajectory produced in Exercise 2: My first metadynamics simulation. Notice that you have to specify the value of \(k_BT\) in energy units. While running your simulation this information was communicated by the MD code.
As a result, PLUMED will produce a new COLVAR_REWEIGHT file with one additional column containing the metadynamics bias potential \( V(s) \) calculated using all the Gaussians deposited along the entire trajectory. You can easily obtain the weight \( w \) of each frame using the expression \(w\propto\exp\left(\frac{V(s)}{k_BT}\right)\) (umbrella-sampling-like reweighting). At this point, you can read the COLVAR_REWEIGHT file using a python notebook and compute a weighted histogram or, alternatively, if you want PLUMED to do the weighted histograms for you, you can add the following lines at the end of the plumed_reweight.dat file and re-run PLUMED driver:

# Use the metadynamics bias as argument as: REWEIGHT_BIASARG=__FILL__ # Calculate histograms of phi and psi dihedrals every 50 steps # using the weights obtained from the metadynamics bias potentials (umbrella-sampling-like reweighting) # Look at the manual to understand the parameters of the HISTOGRAM action! hhphi: HISTOGRAMcompulsory keyword ( default=*.bias ) the biases that must be taken into account when reweightingARG=phithe input for this action is the scalar output from one or more other actions.STRIDE=50compulsory keyword ( default=1 ) the frequency with which the data should be collected and added to the quantity being averagedGRID_MIN=-picompulsory keyword the lower bounds for the gridGRID_MAX=picompulsory keyword the upper bounds for the gridGRID_BIN=50the number of bins for the gridBANDWIDTH=0.05compulsory keyword the bandwidths for kernel density estimationLOGWEIGHTS=as hhpsi: HISTOGRAMlist of actions that calculates log weights that should be used to weight configurations when calculating averagesARG=psithe input for this action is the scalar output from one or more other actions.STRIDE=50compulsory keyword ( default=1 ) the frequency with which the data should be collected and added to the quantity being averagedGRID_MIN=-picompulsory keyword the lower bounds for the gridGRID_MAX=picompulsory keyword the upper bounds for the gridGRID_BIN=50the number of bins for the gridBANDWIDTH=0.05compulsory keyword the bandwidths for kernel density estimationLOGWEIGHTS=as # Convert histograms h(s) to free energies F(s) = -kBT * log(h(s)) ffphi: CONVERT_TO_FESlist of actions that calculates log weights that should be used to weight configurations when calculating averagesGRID=hhphi ffpsi: CONVERT_TO_FEScompulsory keyword the action that creates the input grid you would like to useGRID=hhpsi # Print out the free energies F(s) to file once the entire trajectory is processed DUMPGRIDcompulsory keyword the action that creates the input grid you would like to useGRID=ffphicompulsory keyword the action that creates the grid you would like to outputFILE=ffphi.dat DUMPGRIDcompulsory keyword ( default=density ) the file on which to write the grid.GRID=ffpsicompulsory keyword the action that creates the grid you would like to outputFILE=ffpsi.datcompulsory keyword ( default=density ) the file on which to write the grid.
You can now compare the free energies as a function of \( \phi \) calculated:
Are the two free energies identical?
In the previous exercise, we calculated the final bias \( V(s) \) on the entire metadynamics trajectory and we used this quantity to calculate the correct statistical weight of each frame, which is needed to reweight the biased simulation. In this exercise, the user will learn how this information can be used to calculate the error in the reconstructed free energies and assess whether the simulation is converged or not.
Let's first:
COLVAR_REWEIGHT file obtained at the end of Exercise 3: Reweighting (unbiasing) a metadynamics simulation;phi.weight) containing the value of the dihedral \( \phi \) and the corresponding (un-normalized) weight \( w \) for each frame of the metadynamics trajectory.At this point we can apply the block-analysis technique (for more info about the theory, have a look at PLUMED Masterclass 21.2: Statistical errors in MD) to calculate the average free energy across the blocks and the error as a function of block size. For your convenience, the do_block_fes.py python script provided in the data directory of the GitHub repository of this Masterclass can be used to read the phi.weight file and produce the desired output. The users should properly choose the following input parameters:
# Arguments of do_block_fes.py # - FILE: input file with 2 colums containing the CV value and weight for each frame of the trajectory # - NCV: number of CVs # - MIN/MAX: CV range # - NBIN: # points in output free energy # - KBT: temperature in energy units (kJoule/mol) # - N: Block size # python3 do_block_fes.py FILE NCV MIN MAX NBIN KBT N
and run the above script for different block sizes ranging from 1 to 1000. For each choice of block size, the script will produce an output file, which contains 3 colums:
At this point, the users should:
The users should verify that the error increases with the block size (why?) until it reaches a plateau when the dimension of the block exceeds the correlation time between data points. If a plateau is not observed, then the simulation is not converged yet and should be run a bit longer.
From this analysis, what can we say about the convergence of the metadynamics simulation performed in Exercise 2: My first metadynamics simulation ?
In the previous exercises, we have performed a metadynamics simulation on alanine dipeptide using the backbone dihedral \( \phi \) as CV. We have analyzed the simulation and noticed that:
These two observations indicate that our simulation is converged and that the dihedral \( \phi \) can be considered a good CV. A good set of CVs for metadynamics should indeed:
Identifying a priori a good set of CVs to describe a specific problem is far from trivial. In this exercise, the users will learn how to detect potential problems in their choice of CV(s). Let's first perform additional 1D metadynamics simulations using one of the following CVs:
The users are invited to prepare, for each of the CV listed above, a PLUMED input file to perform a 1D well-tempered metadynamics simulation, execute the simulation, and analyse the results in terms of:
and compare the results with the previous simulation in which \( \phi \) was used as the metadynamics CV. Based on this analysis, can you discriminate between good from bad CVs?
To complete this exercise, the users should define and test a new CV that is either:
Please post the results of your simulations on Slack!
In this last exercise, we will tackle a real-life biological problem: studying the conformational transition of a complex biological system. The system that we are going to study is the C-terminal domain (CTD) of the RfaH virulence factor from Escherichia coli. This part of the system, which we refer to as RfaH-CTD, undergoes a dramatic conformational transformation from β-barrel to α-helical, which is stabilized by the N-terminal domain of the RfaH virulence factor (see Fig. masterclass-21-4-RfaH-CTD-fig).
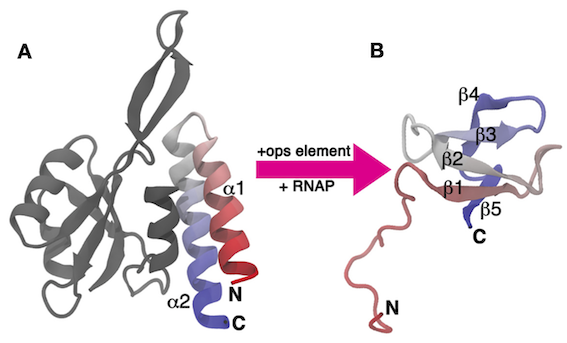
In the data/RfaH-CTD folder of the GitHub repository of this Masterclass, you will find:
topol.tpr file, which is needed to perform a MD simulation of this sytem with GROMACS.The objective of this exercises are to:
In order to complete the exercise, the students should:
Please keep in mind that:
BIASFACTOR.Finally, due to the special nature of the force field, please execute GROMACS using the following command:
gmx mdrun -plumed plumed.dat -ntomp 4 -noddcheck
You can adjust the number of CPU cores you want to use (here 4, OpenMP parallelization), based on the available resources. The system is not particularly big, therefore using a large number of cores might be inefficient.
Please post the results of your simulations on Slack!